
29 May How to Reasonably Choose HDPE and LLDPE Geomembrane?
Choosing between HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and LLDPE geomembranes(Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) for a project depends on several factors, including the specific requirements of the project, environmental conditions, and the properties of each type of geomembrane. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision:
Key Considerations
- Project Requirements
- Application Type: Identify the primary function of the geomembrane in your project. Common applications include containment (e.g., landfills, ponds), liners (e.g., canals, reservoirs), and barriers (e.g., gas barriers, root barriers).
- Chemical Resistance: Determine the chemical environment the geomembrane will be exposed to, such as exposure to hydrocarbons, acids, or other chemicals.
- UV Resistance: Consider the level of UV exposure the geomembrane will face. Projects with high UV exposure require materials with better UV resistance.
- Mechanical Stress: Assess the mechanical stresses the geomembrane will endure, such as punctures, tears, and tensile forces.
- Material Properties
- Thickness: Evaluate the required thickness based on the application and expected stresses. HDPE geomembranes typically range from 0.5mm to 3mm in thickness, while LLDPE is often available in similar thicknesses.
- Flexibility: LLDPE geomembrane are generally more flexible than HDPE, making them easier to install in projects with complex shapes or contours.
- Durability: HDPE geomembranes are known for their durability and high resistance to chemicals and UV radiation, making them suitable for harsh environments.
- Weldability: Consider the ease of welding and seam integrity. Both HDPE and LLDPE can be welded, but LLDPE’s flexibility often results in better seam performance.
LLDPE Geomembrane
HDPE Geomembrane
Comparison of HDPE and LLDPE Geomembranes
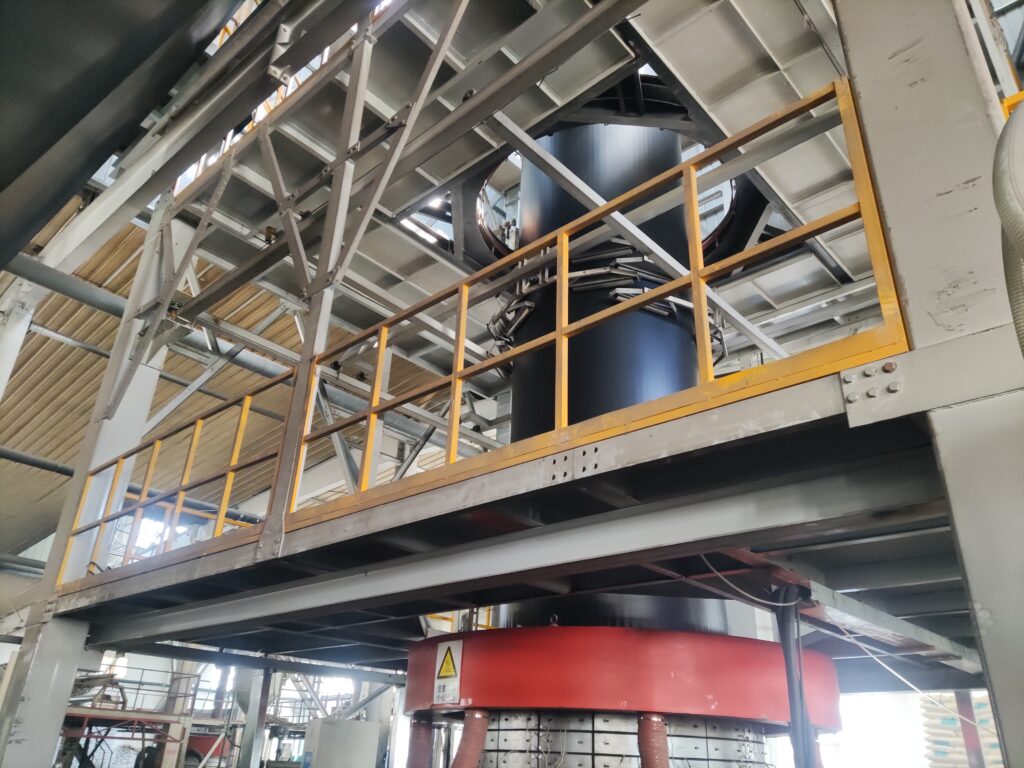

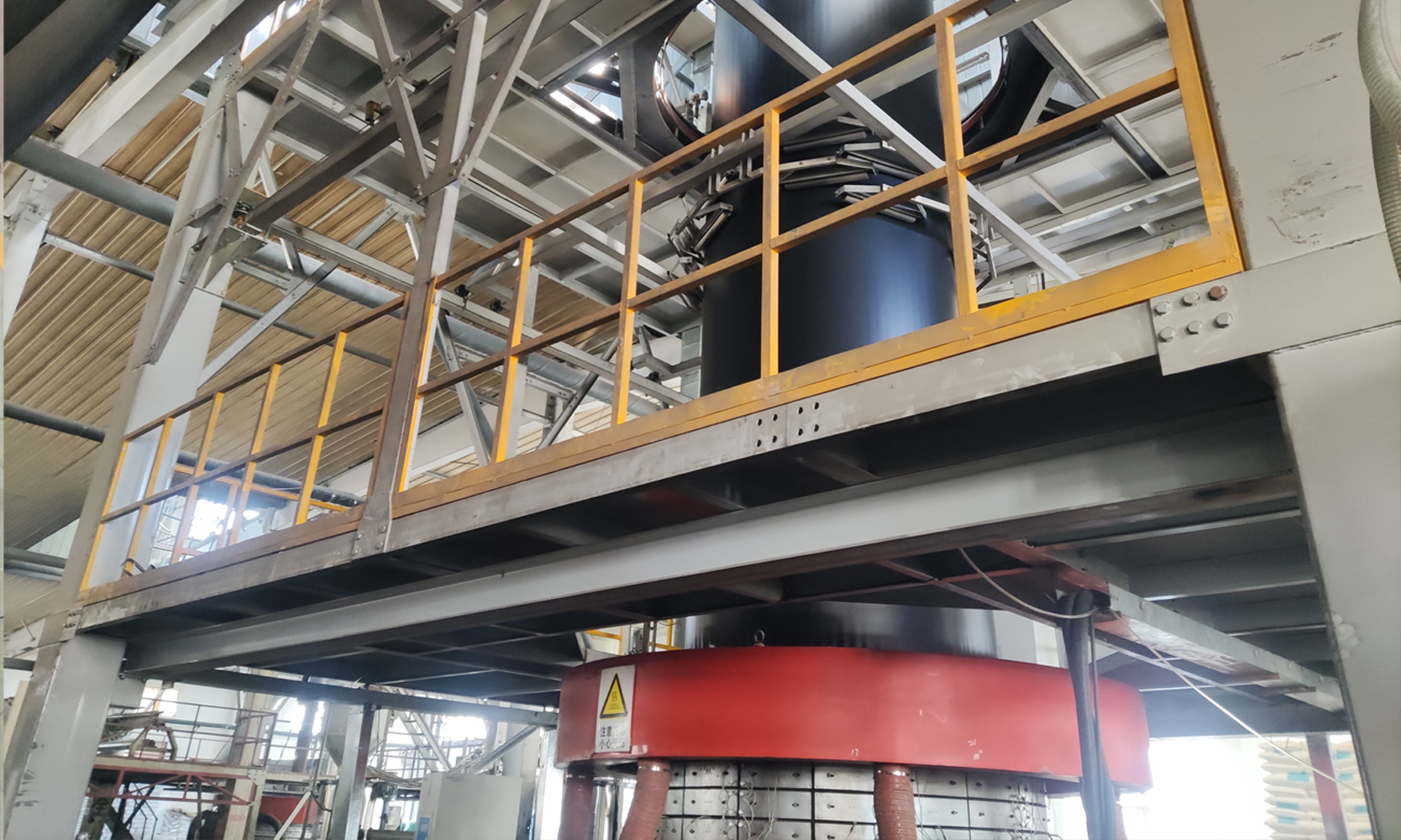
Geomembrane Production Equipment
| Property | HDPE Geomembrane | LLDPE Geomembrane |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
| Tensile Strength | Higher | Lower, but still strong |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Very good |
| UV Resistance | Excellent | Good to very good |
| Puncture Resistance | High | Very high |
| Weldability | Good, requires precision | Better, easier to weld |
| Cost | Typically lower | Typically higher |
Application Scenarios
- HDPE Geomembrane
- Landfill Liners and Caps: HDPE’s high chemical resistance and durability make it ideal for containing solid and hazardous waste.
- Mining: Suitable for heap leach pads and tailings containment due to its robustness and chemical resistance.
- Aquaculture: Used in fish and shrimp pond liners for its durability and resistance to punctures.
- LLDPE Geomembrane
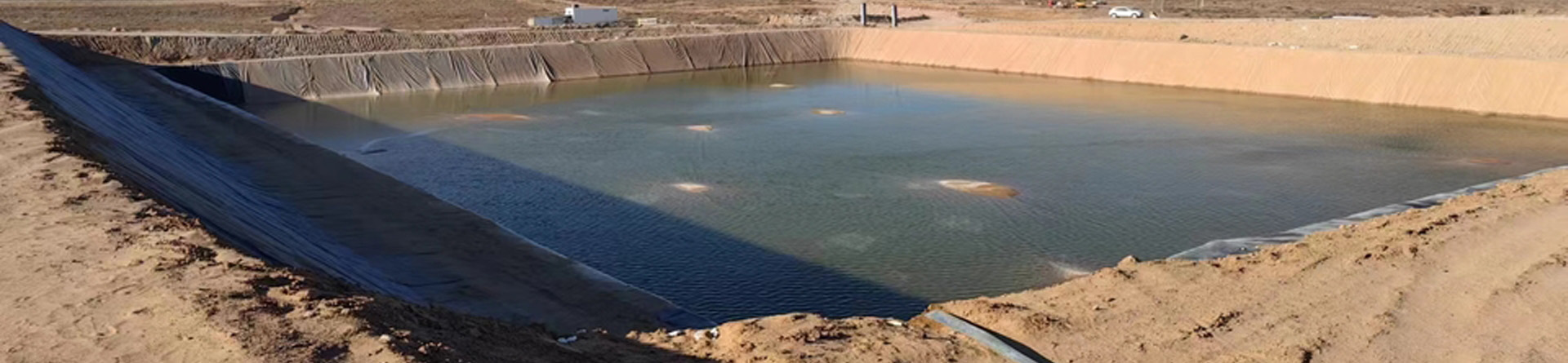
- Canals and Ponds: Its flexibility makes LLDPE ideal for lining canals, ponds, and other water containment systems with complex shapes.
- Agricultural Applications: Used in applications like irrigation ponds and liners where flexibility and ease of installation are critical.
- Secondary Containment: Suitable for secondary containment systems due to its excellent puncture resistance and flexibility.
Decision Process
- Site Assessment
- Evaluate the specific conditions of the site, including soil type, climate, and exposure to chemicals or UV radiation.
- Material Testing
- Conduct compatibility tests if the geomembrane will be in contact with specific chemicals or environmental conditions.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Compare the costs of HDPE and LLDPE geomembranes, considering not just the material cost but also installation, maintenance, and lifespan.
- Consult with Experts
- Engage with engineers, contractors, and suppliers who have experience with both materials to get their insights and recommendations based on similar projects.
Conclusion
Choosing between HDPE and LLDPE geomembranes depends on a thorough understanding of your project’s requirements and the specific properties of each material. HDPE is preferred for applications requiring high chemical and UV resistance, while LLDPE is favored for its flexibility and ease of installation. By considering the factors outlined above, you can make a well-informed decision that ensures the success and longevity of your project.


Colt4638
Posted at 01:10h, 01 MayVery good https://is.gd/N1ikS2
Grant342
Posted at 01:15h, 01 MayGood https://is.gd/N1ikS2