10 Jun Guide to Choosing the Thickness of HDPE Liners
CChoosing the thickness of (High-Density Polyethylene) HDPE liners depends on several factors, including the application, the type of material being contained, site conditions, and regulatory requirements. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you determine the appropriate thickness for your HDPE liner:
1. Identify the Application
Different applications require different liner thicknesses. Common applications include:
- Landfills
- Mining
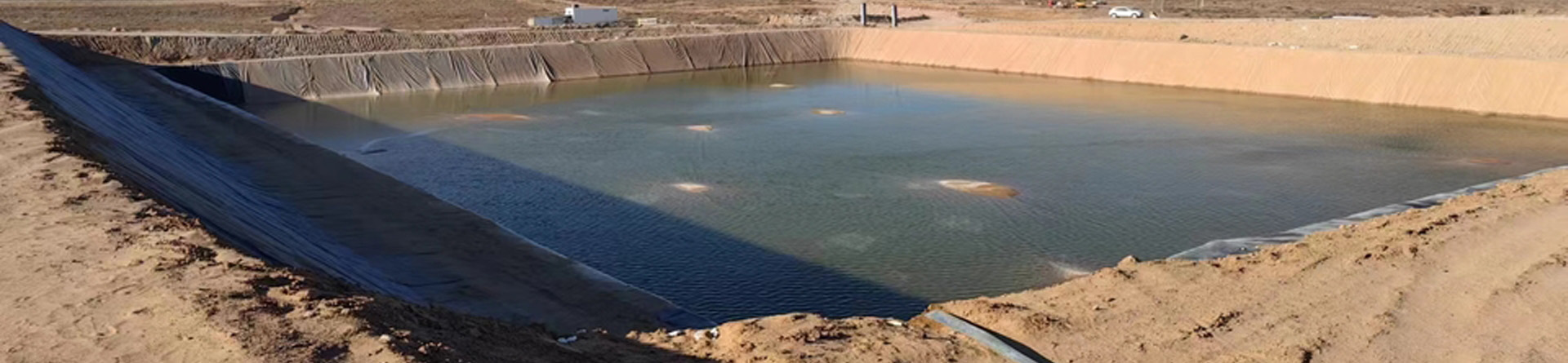
- Ponds and reservoirs
- Wastewater treatment
- Secondary containment
2. Determine the Type of Material Being Contained
The chemical composition and physical properties of the material being contained will influence the required thickness. For example:
- Hazardous waste may require thicker liners.
- Water containment typically requires less thickness compared to chemical containment.
3. Evaluate Site Conditions
Consider the following site conditions:
- Subgrade conditions: Rough or rocky subgrades may necessitate thicker liners to prevent punctures.
- Load conditions: Higher loads or pressure (e.g., in landfill applications) may require thicker liners to withstand the stress.
4. Check Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory agencies often have minimum thickness requirements for different applications. Ensure compliance with local, state, and federal regulations.
5. Assess Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as UV exposure, temperature variations, and potential for chemical exposure should be considered. Thicker liners may provide better resistance to environmental stresses.
HDPE Geomembrane Liners
6. Consider HDPE Liners the Durability and Longevity Required
For long-term projects, a thicker liner may be more durable and provide a longer lifespan.
7. Review Manufacturer Recommendations
Consult with liner manufacturers for their recommendations based on the specific use case. Manufacturers often have guidelines and technical support to assist in selecting the appropriate thickness.
Typical Thickness Guidelines
Here are some general guidelines for common applications:
- Ponds and Reservoirs: 0.5 mm to 1.5 mm (20 mil to 60 mil)
- Landfills:
- Base liners: 1.5 mm to 2.0 mm (60 mil to 80 mil)
- Cover systems: 1.0 mm to 1.5 mm (40 mil to 60 mil)
- Mining Applications: 1.5 mm to 2.5 mm (60 mil to 100 mil)
- Wastewater Treatment: 1.0 mm to 2.0 mm (40 mil to 80 mil)
- Secondary Containment: 1.5 mm to 2.5 mm (60 mil to 100 mil)
Example Calculation
Let’s assume you’re lining a pond:
- Application: Pond
- Material: Freshwater
- Site Conditions: Smooth, sandy subgrade
- Environmental Factors: Moderate UV exposure
For this scenario, a liner thickness of 1.0 mm (40 mil) would generally be suitable, balancing cost and durability.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct thickness for an HDPE liner involves assessing the specific requirements of your project, including application, material characteristics, site conditions, regulatory guidelines, and environmental factors. Consulting with manufacturers and considering industry standards will help ensure the right choice for your project’s needs.
If you are looking for a supplier of HDPE Liners, please contact us via the form below.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.